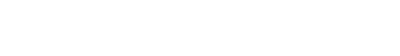When an electric arc furnace is working, arc heat of a temperature of 3,000 to 7,000°C is generated.
While the average temperature of a general waste incinerator is 800ºC, using this "ultra-high temperature" makes it possible to safely and reliably melt and completely detoxify waste.
Based on the desire to make better use of the characteristics of electric arc furnaces in promoting initiatives for recycling, energy saving and environmental conservation, we have been a pioneer in the material recycling business for over 30 years.
We utilize electric arc furnace operation technology to detoxify waste and at the same time recycle steel resources as part of steel products.
We believe that promoting resource recycling, which is a system to properly process ever-increasing waste and produce products, is an important mission that we must fulfill as a corporate citizen.
Our material recycling business started from the treatment of medical waste, such as injection needles and surgical scalpels, and gradually increased the number of items to treat, reflecting the expanding needs of the times. Material recycling has now become a pillar of our Group’s business.
In recent years, in addition to the introduction of a new crusher (Yamaguchi Division) in order to carry out stable treatment of carbon fiber (CFRP), we introduced destructive treatment of CFC gas, waste treatment and fuel gas production by a gasification furnace, and waste drinking water treatment using neutralizing equipment. Through these initiatives, our material recycling has evolved into a business that is capable of comprehensively provide a wide variety of waste treatment services.
We will continue to contribute to resource recycling and environmental conservation in Japan through our comprehensive recycling system centered on electric arc furnaces.
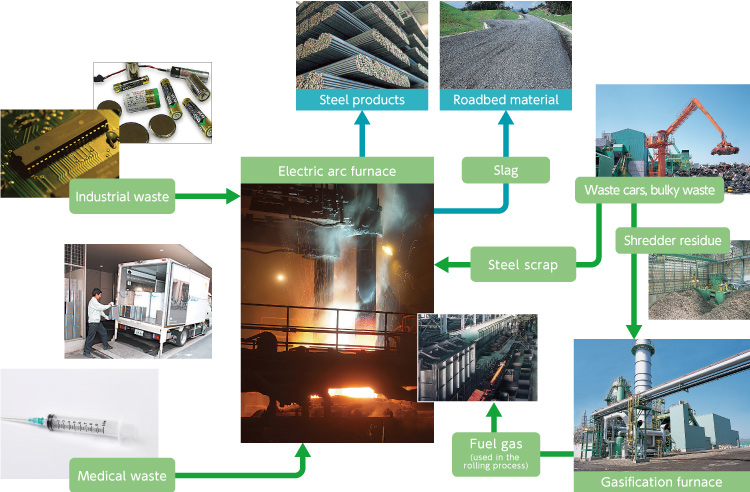
The MESSCUD system: medical waste treatment system, the starting point of our material recycling business
At that time in 1980, many used injection needles were illegally dumped, causing infection, and became a serious social problem.
While the number of medical appliances made of materials that were not suitable for heat sterilization, such as plastics and electronic devices, was increasing, many appliances were thrown away after use in order to isolate the portions that had come into contact with patients.
Seeing a media report on this trend, one of our employees thought, “We can melt dangerous items in an electric arc furnace.” This was the beginning of MESSCUD.
To carry out and receive income for the disposal of items that had been incinerated by local governments, we, as a private business, faced many obstacles to overcome, including gaining the understanding of medical circles.
While honestly explaining the seriousness of the social problem, we developed safe and secure treatment processes.
Our MESSCUD business started in 1988.
Following the establishment of the “Infectious Waste Management Manual based on the Waste Management Law” in accordance with the revision of the Waste Management Law in 1992, MESSCUD surged in popularity overnight.
Today, it is recognized as a safe and sustainable treatment method, supported by many customers.

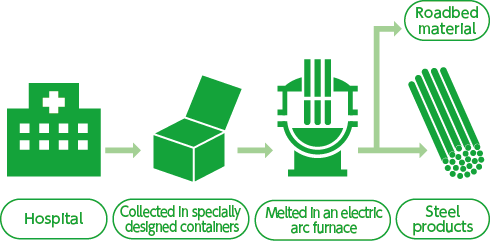
Waste discharged from medical institutions, such as injection needles, syringes and scalpels, may carry a risk of infection and thus require special treatment.
For this reason, such waste was conventionally managed separately from general waste at medical institutions, where dangerous operations, such as removing injection needles and sorting drug containers and medical equipment, took place.
The MESSCUD system (patented) developed by Kyoei Steel uses an electric arc furnace, which generates high-temperature heat, to melt medical waste together with the containers.
The containers are made of steel, which can be attracted by a magnet, so workers do not need to directly touch the waste in all processes from collection to disposal.
Communication with the medical frontline enabled us to prepare containers of four different sizes and also develop a stand with a lid that can be opened and closed silently with a pedal. Thus we made several improvements to the system in consideration of the hygiene of the medical staff and patients.
The system’s dedicated containers placed in medical institutions nationwide are collected via affiliated agencies, to be detoxified and melted safely and securely in electric arc furnaces.
In 2002, the MESSCUD Medical Treatment Safety Fund was established.
We donate a part of our sales to various organizations through the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and other organs.

To electric arc furnaces with steel scrap